Introduction
One of the most persistent and fascinating anatomical myths is the question: do women have more ribs than men? This notion has permeated cultures for centuries, often blending religious teachings, cultural stories, and scientific misunderstanding into a single pervasive belief. The idea that men and women have a different number of ribs, particularly the belief that women have more ribs than men, stems largely from the Biblical account of Adam and Eve. According to the Book of Genesis, Eve was created from one of Adam’s ribs, leading many to conclude that men might be left with fewer ribs than women.
However, modern anatomy and medical science firmly refute this concept. Both men and women have the same number of ribs. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the origins of the myth, outline the scientific truth about human ribs, and discuss anatomical variations, medical conditions, and cultural beliefs that have helped keep this question alive. If you have ever wondered, this article will give you a thorough and clear answer.
Understanding Human Rib Anatomy
To fully address the question, do women have more ribs than men, it is essential to first understand the basic anatomy of the human ribcage.
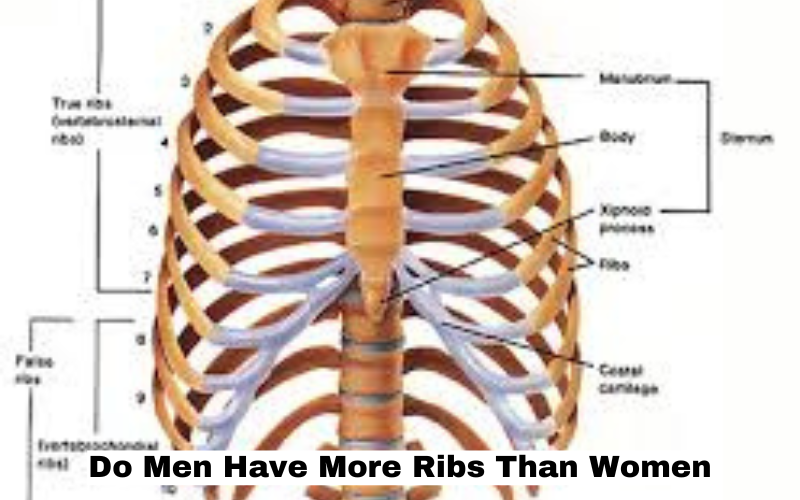
- The human ribcage is made up of 24 ribs, forming 12 pairs.
- Each rib pair connects at the back to the thoracic vertebrae.
- Most ribs also connect to the sternum through costal cartilage, helping form the protective thoracic cage.
The ribcage serves vital functions, including:
- Protection: Safeguarding critical organs such as the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels.
- Support: Helping to maintain the structure and posture of the upper body.
- Respiration: Expanding and contracting with the lungs during breathing.
Most importantly, these anatomical features are the same in both men and women.
Do Men and Women Have the Same Number of Ribs?
The definitive and scientifically confirmed answer to whether women have more ribs than men is: No.
- Both men and women have 24 ribs in total, organized into 12 pairs.
- The number of ribs does not differ based on sex.
- Any natural variation in rib count is due to rare congenital anomalies, not gender.
Despite differences in height, weight, muscle mass, and body composition, the rib count remains consistent across healthy men and women. This fundamental fact is taught in basic anatomy classes, confirmed through countless medical imaging studies, and recorded in medical literature.
Why Do Some People Believe Women Have More Ribs Than Men?
The persistent myth that women have more ribs than men primarily comes from religious interpretations—most notably from the Biblical story in Genesis, which states that God created Eve from one of Adam’s ribs.
- This story, when taken literally, led to the assumption that all men inherited one fewer rib.
- Over centuries, this belief became ingrained in some cultural narratives, even though it has no biological basis.
Importantly, removing a rib in an individual does not alter their offspring’s genetic code. Modern genetics ensures that all humans inherit the same basic anatomical template — 24 ribs, regardless of sex.
How Science Disproved the Rib Myth
Scientific study and medical imaging technology (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) have thoroughly demonstrated that:
- Men and women both possess 24 ribs.
- Rib counts are not influenced by sex.
- Rib counts only vary in cases of rare congenital anomalies.
Doctors, anatomists, and scientists have been aware of this for centuries, yet the myth endures, especially in religious and cultural contexts.
Anatomical Classification of Ribs
To better understand the ribcage and clarify the topic, let’s break down the three types of ribs found in both sexes:
1. True Ribs
- Pairs 1-7
- Directly attach to the sternum via costal cartilage.
- Provide the main structural protection for the heart and lungs.
2. False Ribs
- Pairs 8-10
- Attach indirectly to the sternum by connecting to the cartilage of the rib above.
- Offer additional protection and flexibility.
3. Floating Ribs
- Pairs 11-12
- Do not attach to the sternum at all.
- Primarily function as muscle attachment points.
Rib Variations – When Does Rib Count Change?
The only natural variations in rib count result from rare congenital conditions, not sex differences.
Cervical Ribs
- An extra rib sometimes forms above the first rib.
- Found in about 1 in 500 people.
- More common in women, but still unrelated to overall rib count between sexes.
Missing Ribs
- Occasionally, individuals are born missing a rib pair, but this occurs regardless of sex.
- Certain syndromes (like Goldenhar Syndrome) can cause rib abnormalities.
These rare exceptions do not support the idea that women have more ribs than men.
Do Women’s Ribs Change During Pregnancy?
Pregnancy can temporarily alter the position and flexibility of a woman’s ribcage, but it does not change the actual rib count.
- Pregnancy hormones like relaxin cause ligaments and cartilage to soften.
- This allows the ribcage to expand, accommodating the growing uterus and increased lung capacity.
- After childbirth, the ribcage returns to its pre-pregnancy state.
This temporary adjustment is often misinterpreted, but it has nothing to do with the actual number of ribs.
Common Rib-Related Medical Conditions
Rib Fractures
- Caused by trauma, accidents, or falls.
- Affect men and women equally.
- Treatment includes pain management and monitoring for complications like pneumothorax.
Costochondritis
- Inflammation of rib cartilage, causing chest pain.
- More common in women, especially after physical strain.
Osteoporosis
- More likely to affect postmenopausal women, making ribs more fragile.
- Supplements and weight-bearing exercise can reduce risk.
Historical Roots of the Rib Myth
The belief that women have more ribs than men is directly tied to:
- Literal interpretations of Biblical texts.
- Early religious influence on anatomical studies.
- Cultural transmission of folk anatomy in non-medical communities.
Even in some modern religious education, the myth persists, despite overwhelming scientific evidence to the contrary.
Regeneration – A Unique Rib Feature
Interestingly, ribs have a unique ability to regenerate after surgical removal — provided the periosteum (outer membrane) is left intact.
- Surgeons frequently use rib bone for grafts.
- Within months, the removed rib can regrow completely.
This remarkable trait applies equally to men and women.
See Also: Do Men Have Less Ribs Than Women
FAQ’s
Q1. Do women have more ribs than men?
No, both men and women have 24 ribs (12 pairs).
Q2. Can removing a rib change future generations?
No, removing a rib does not change genetic inheritance.
Q3. Do all humans have 24 ribs?
Most do, but rare congenital conditions can lead to extra or missing ribs.
Q4. Do women’s ribs change during pregnancy?
The ribcage expands temporarily, but the rib count stays the same.
Q5. Why does the myth persist?
It stems from religious stories and cultural misconceptions, not science.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to the question of whether women have more ribs than men is an unequivocal no. Both men and women have 24 ribs — 12 pairs each. The idea that women have more ribs than men originates from religious stories, not from medical or anatomical fact. Modern science has thoroughly debunked this notion, yet it persists due to cultural traditions and misunderstood historical texts.
Understanding the truth about rib anatomy helps dispel these myths and fosters a more accurate understanding of human biology. Whether you’re curious due to religious questions or simply fascinated by anatomy, the science is clear: men and women have the same number of ribs.





One thought on “Do Men Have More Ribs Than Women? Separating Myths from Scientific Facts About Human Anatomy”